Welcome to our comprehensive guide on electronic scrap purchase prices and sorting criteria. This resource is designed to give you detailed insights into the world of electronic waste recycling, including how to determine the value of your electronic scrap and the best practices for sorting and preparing it for sale.
Factors Influencing Electronic Scrap Prices
Electronic scrap prices are influenced by various factors including the type of material, the current market demand for precious metals, and the condition of the electronic components.
Common Types of Electronic Scrap
Identify the most common types of electronic scrap, from old cell phones to obsolete computers, and understand how each type is valued differently.

Ceramic CPU Goldcap processors, along with older 286, 386, or 486 ceramic processors from computers or industrial computers, are the focus of this category. These processors should be free of any attachments like fans or heat sinks to qualify.

This category is dedicated to ceramic CPU Intel and AMD processors extracted from computers or industrial computers, and they should not have any additional components like fans or heat sinks attached. Notably, for AMD ceramic processors,

This category encompasses plastic CPU processors sourced from computers, notebooks, and industrial computers, and they should be free of any extra components like fans or heat sinks. These CPUs are typically found in black, green, or brown colors.
Additionally, plastic CPUs, predominantly green, that still retain their cooling plates and haven't been detached, are evaluated at a distinct purchase price.

Plastic CPU processors equipped with cooling plates, originating from computers, notebooks, or industrial computers, are included in this category. These processors may also have additional attachments such as fans or heat sinks. Commonly found in colors like black, green, or brown, these CPUs with their integrated cooling components are a specific focus of our purchasing criteria.

PCB and slot processors sourced from computers or industrial computers form this category. These components should be free of any external attachments, including housings, fans, or heat sinks, to qualify.


Now that you have the gold plated pins all separated from the body, it is time to separate the gold from the base metals. As said before, the most common base metals that are present in the pins are 'Kovar' (Fe+Co+Ni) alloy, the solder (Sn+Pb/Sn+Ag) and Copper. The separation is done chemically by boiling the pins in a solution of 32% Hydrochloric acid (HCl).

This category encompasses RAM/main memory modules extracted from computers or industrial computers, broadly classified into two types:

This category includes Chips, Eproms, and ICs extracted from computers or industrial computers. For standard black chips, we classify them into two distinct types:
Additionally, we deal with special chips and components, such as telephone chips, bank card chips, SIM cards, etc. For bulk quantities, the pricing is determined based on the precious metal content they contain.
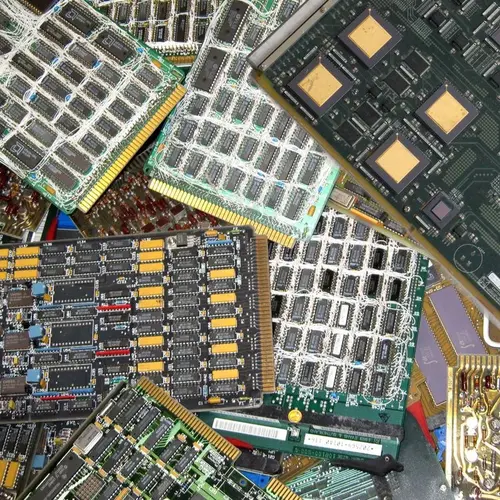

Class 1-A PCBs refer to older models of printed circuit boards characterized by their galvanic gold-plated contacts or connector strips. These boards are typically harvested from obsolete mainframe computers or servers and are known for their densely populated arrangement of small chips. It's essential that these circuit boards are intact and not stripped of any components. However, any attached metal sheets, frames, or heat sinks should be detached before processing.
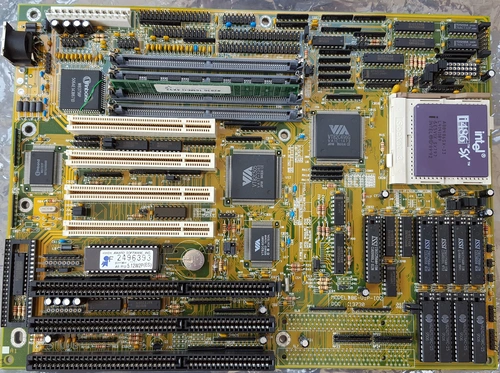
Class 1-B PCBs refer to circuit boards derived from computers or industrial machinery that exhibit visible gold plating along with an abundance of chips, transistors, and plug-in contacts rich in precious metals. This category specifically includes motherboards and plug-in cards, such as sound and graphics cards, provided they were produced prior to the year 2000. Prior to processing, any metal sheets and heat sinks are detached, and batteries are also carefully removed.
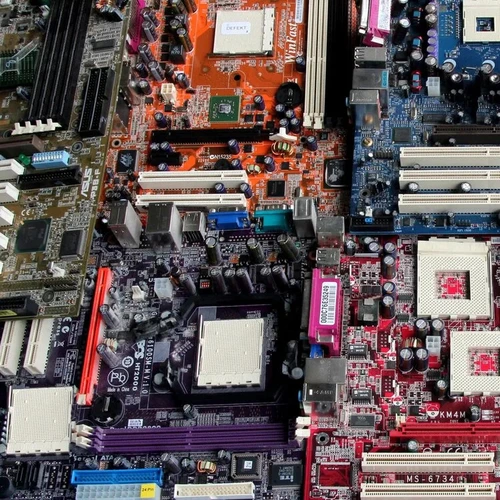
Class 1-D PCBs encompass a vibrant array of motherboards without any attached components, deriving from various computers. These boards are notable for their colorful presentations in shades like yellow, blue, orange, purple, and the traditional green. This category specifically targets motherboards, along with graphics and sound cards produced from 2020 or later, starting from the Pentium 4 or AMD Athlon PC generations. Additionally, this class includes Class 1-A, 1-B PCBs and 1-C PCBs where ferrous and aluminum attachments such as metal sheets and heat sinks remain intact, or those from which valuable components like chips have been extracted.
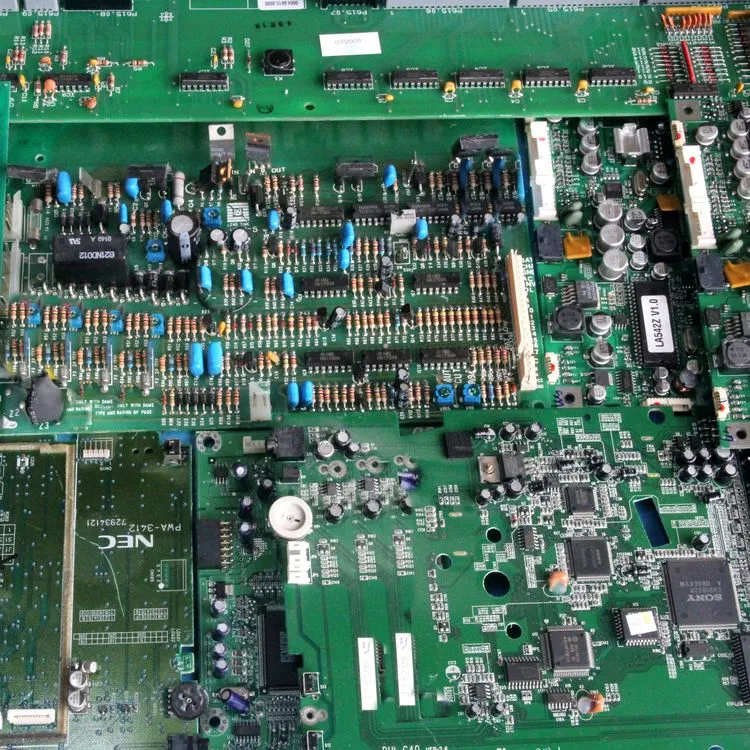

Class 2-A PCBs originate from industrial equipment and are distinct from Class 1 PCBs due to the minimal presence of visible gold contacts. These circuit boards are populated with small chips enriched with precious metals, alongside transistors and quartz crystals. However, they must be free of any large components such as heat sinks, transformers, or capacitors exceeding the size of a thumb. This class also encompasses Class 1-C PCBs that still have their attachments intact.
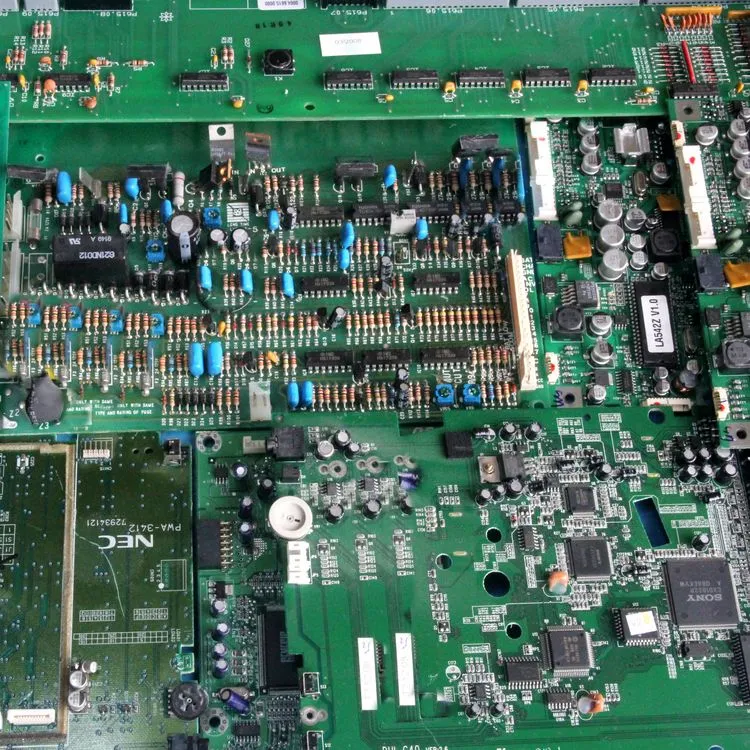

Class 2-B PCBs are derived from industrial equipment and are characterized by their minimal visible gold contacts, setting them apart from Class 1 PCBs. These boards come equipped with a select number of chips that house precious metals, as well as transistors and quartz crystals. Unlike other classes, they may sometimes include attached components such as heat sinks, transformers, or relays, albeit in lesser quantities compared to other categories.
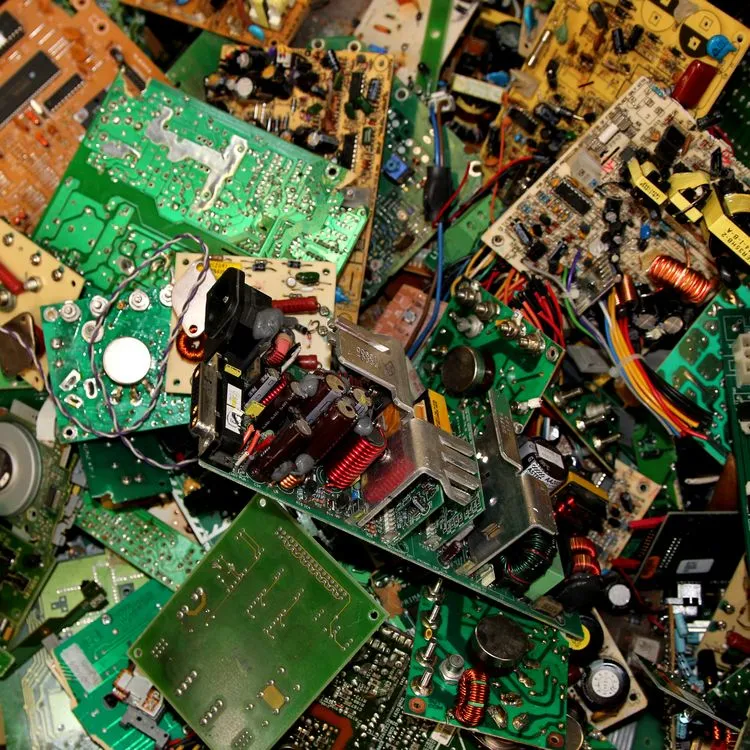

Class 2-A PCBs originate from industrial equipment and are distinct from Class 1 PCBs due to the minimal presence of visible gold contacts. These circuit boards are populated with small chips enriched with precious metals, alongside transistors and quartz crystals. However, they must be free of any large components such as heat sinks, transformers, or capacitors exceeding the size of a thumb. This class also encompasses Class 1-C PCBs that still have their attachments intact.

Class 3 PCBs are boards with large components such as capacitors, transformers, heat sinks and only a few components / chips or contacts containing precious metals. They originate mostly from monitors, power supply controls or consumer electronics. They also include class 1-And 2 PCBs if they contain very large / heavy attachments.